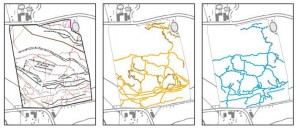
Electromagnetic induction (EMI) on a conflict landscape of the Great War: Chemin du Mont de la Hutte, Ploegsteert
In spite of an increase in World War I-related excavations in Flanders (Belgium), little is known about the nature and extent of the buried heritage of WWI from research on a landscape scale. This paper examines the combination of historical aerial photographic evidence and geophysical soil sensing. A case study in Comines-Warneton compares data derived from contemporary WWI aerial photographs with multi-receiver electromagnetic induction surveys. This comparison provides an understanding of the degree of preservation of trenches, dugouts and other military structures, and illustrates the added value of integrating both techniques in an in-depth, non-invasive study of conflict landscapes.